Innovative Solutions for Enhanced Climate Resilience: Pilot Projects for Flexible Infrastructure Elements
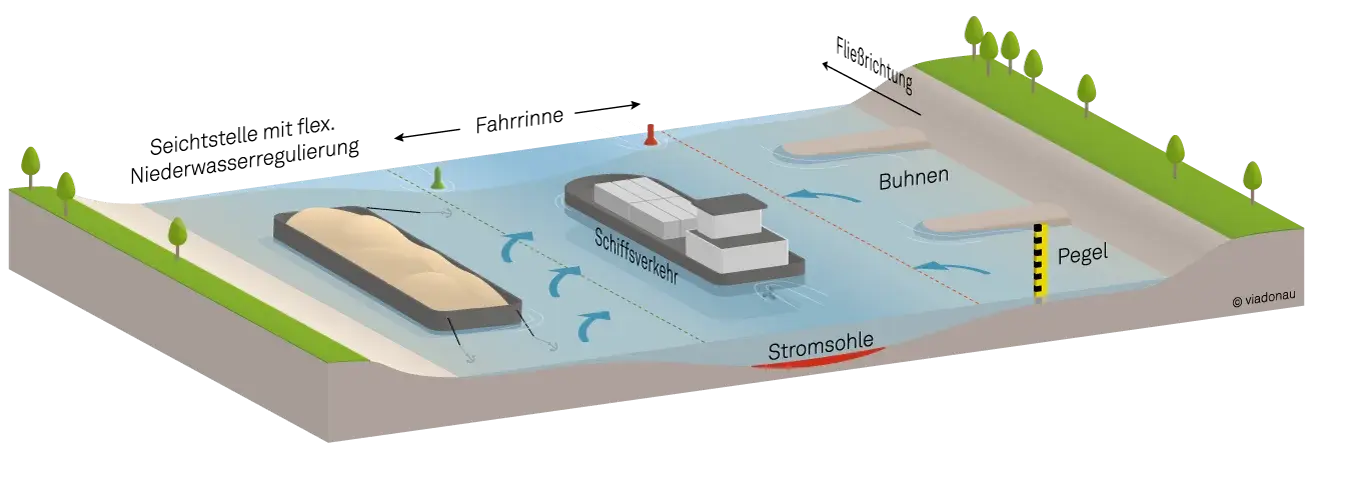
The free-flowing sections of the Danube, known for their dynamic nature, experience ongoing erosion and sedimentation. Innovative methods have been developed to complement traditional river engineering tools. These methods include changes in sediment management, transporting dredged material upstream, and the creation of artificial islands to increase velocity in shallow sections, providing ecological benefits simultaneously.
However, longer low water periods due to climate change, bring a new challenge for dealing with shallow sections of the Danube. Within the framework of FAIRway Danube II we are pleased to carry out pilot tests for flexible infrastructure elements in shallow sections in the Danube. This innovative approach offers a non-invasive, near natural solution for low water periods, promising an increase in fairway depth.
Based on an technique already used in 1890 the modern interpretation of the flexible infrastructure elements is very promising and will contribute to a more resilient Danube in the future.
The implementation of these projects across Austria, Croatia, Romania, and Bulgaria marks a significant step toward achieving sustainable and adaptable waterway management.
Key Objectives and Benefits
- Climate Change Resilience
The flexibility inherent in these infrastructure elements is designed to adapt to the dynamic challenges posed by climate change. This ensures a robust and resilient system capable of withstanding fluctuations in water levels. - Near Natural Solution
The innovative approach focuses on non-invasive, near natural solutions, minimizing the impact on habitats and ecosystems. - Increased Fairway Depth
Anticipated benefits include an enhancement of fairway depth during low water periods, contributing to improved navigational reliability and predictability.


