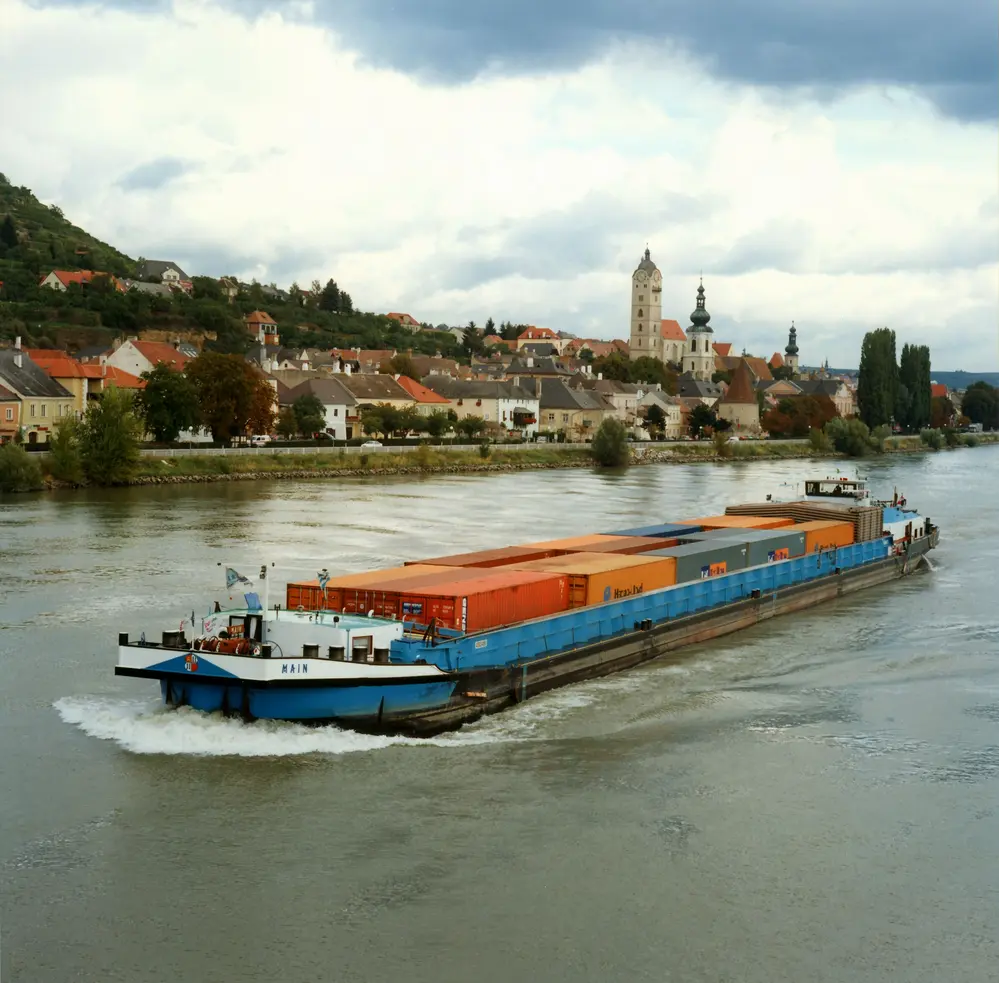
Climate change & shipping
In addition to optimising the environmental performance of inland waterway transport, viadonau also considers the challenges of climate change, within the context of international research projects, to be of great importance.
Climate change could affect the flow regime of the Danube, thereby having a significant effect on the waterway as an infrastructure, flood protection schemes and also the river's ecosystem.
First investigations into the Austrian Danube suggest that, in the medium term, climate change will have a fairly positive impact on inland waterway transport, in particular due to reduced ice formation. Trend analysis relating to to the occurrence of low water, ice formation and reduced visibility show the positive effects of climate change for the period 1950 - 2005. A slight decline is projected until 2050 in terms of the potential for low water events. In the long term, 2050 - 2100, most projections suggest that there may be an increase in possible low-water events.
Predictions concerning extreme flood events in the context of climate change cannot yet be made with sufficient confidence.
In the meantime, more climate change projects, involving viadonau, could be carried out to improve knowledge of the effects that climate change may have, specifically on Upper Austria. In general, the level of knowledge about the impact of climate change on the flow regime of the entire Danube and inland waterway transport is still insufficient and more scientifically based research needs to be carried in order to bring more clarity to this issue.
Another specific priority is the consideration of operational and navigational technical solutions for the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions in inland navigation as a contribution to slowing global warming and the adaptation to changing future fairway conditions.
Based on the results of the projects ECCONET and Platina 3, depiction of climate change impact on incidences of low water, high water, ice formation and visibility for the Middle Rhine, the Rhine-Main-Danube Canal and the Upper Danube.
| Phenomenon | Period | Middle Rhine | Main-Danube-Canal | Upper Danube |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Low water | 1950-2005 | positive | none | positive |
| until 2050 | none | not known | none | |
| until 2100 | negative | negative | negative | |
| High water | 1950-2005 | none | none | none |
| until 2050 | negative | none | negative | |
| until 2100 | negative | none | negative | |
Ice formation | 1950-2005 | positive | positive | positive |
| until 2050 | none | positive | positive | |
| until 2100 | none | positive | positive | |
Visibility (fog) | 1950-2005 | positive | positive | positive |
| until 2050 | not known | not known | not known | |
| until 2100 | not known | not known | not known |
SYNERGETICS
As part of the EU-funded SYNERGETICS project, hydrogen dual-fuel engines are being tested on a crew transfer vessel, while methanol-based propulsion is being developed for a chemical tanker. The feasibility of a fully electric propulsion system based on interchangeable battery packs is being demonstrated on an inland waterway container transporter, while the electrification of the main propulsion system is being evaluated on a cement freighter. In addition, energy management systems for hydrogen fuel cells are being developed. Hydrodynamic improvements will be demonstrated on an inland vessel for dry cargo. The Catalogue of technical solutions for decarbonisation, the Handbook for vessel owners and the Scenarios for policy-makers, which are produced as part of the project, will accelerate the transition to more environmentally friendly modes of operation.
PLATINA

PLATINA4Action is a strategic project for the sustainable development of inland navigation in Europe and as such is part of the Horizon Europe programme. It supports the European Commission in the implementation of the NAIADES European Action Plan, which aims to make inland navigation more sustainable.
WP3 develops and implements an emission labelling scheme for inland waterway vessels to promote transparency and incentivise the introduction of clean technologies. By creating a clear and standardised framework, the label will encourage greener investments, support emission reductions and facilitate compliance with EU environmental policy.
WP4 focuses on identifying, evaluating and supporting the introduction of innovative zero-emission technologies and solutions for inland navigation. The aim is to overcome barriers to implementation through the development of business models, action plans and pilot projects to ensure that these technologies can be introduced on a large scale and make inland navigation more environmentally friendly and sustainable - and to support the development of innovative zero-emission technologies and solutions for inland navigation.
WP5 identifies technology gaps, assesses the maturity of emerging innovations and analyses funding mechanisms needed to support their development. By identifying the areas where investment and research are most urgently needed, the aim is to accelerate the market maturity of sustainable solutions and drive the transition to greener inland navigation.
Platina 3 is the platform for the implementation of the NAIADES III Action Programme. The main objective of the project was to make the bridge towards future research, innovation and implementation needs in inland navigation in Europe. Structured around four fields: Market, Fleet, Jobs & Skills, the project addressed four priority topics for the success of inland navigation:
- Integration & digitalization of IWT in view of modal shift & synchromodality;
- Zero emission, automated & climate resilient fleet;
- Skilled workforce anticipating to zero emission & automation;
- Smart & climate resilient waterway and port infrastructure with clean energy hubs.
The main outcomes of the project were:
- strategic network of key stakeholders based on intensive, structured exchange;
- Roadmap and Implementation Plan for Research & Development for IWT;
- Policy Implementation Plan for IWT.
Selected project results with relevance to climate change and inland navigation:
- D2.2 Options for shallow-water / climate resilient vessels
- D 4.1 Climate change adaptation strategies - information package for European inland waterway and port infrastructure managers
ECCONET
The ECCONET project examined the impact of climate change on inland navigation in Europe with the emphasis on the Rhine-Main-Danube corridor. For this purpose, the results of existing studies were integrated with newly carried out research to develop new meteorological and hydrological calculations and trend analyses. The study focused on, among other things, ship operations, ship engineering, hydraulic engineering activities and methods for the prediction of water conditions.

EWENT
The EWENT project was launched in 2009 and examined the effects of extreme weather events on transportation systems in the European Union. The aim was to identify risks and consequences for the transport sector and determine the financial consequences. Measures were developed to better manage extreme weather events and recommendations were formulated for decision makers from business, infrastructure management and politics.

MOWE IT
MOWE IT was initiated as a result of the EWENT 2012 project. The focus of the project was the identification of "best practices" and the development of appropriate strategies to support transport companies, government agencies and users of the respective transport systems as much as possible.
The aim was to develop appropriate strategies to reduce the impact of natural disasters and extreme weather events on transport services and infrastructure as much possible. The project was coordinated by the Technical Research Centre of Finland and 12 European research institutes and companies from 8 countries, including viadonau.
The recommendations for the inland navigation sector are summarised in the “Guidebook for Enhancing Resilience of European Inland Waterway Transport in Extreme Weather Events”.

Supergreen
In Project SUPER GREEN a number of representatives from European transport corridors analysed ways to improve the environmental performance of the European transport system. The selected corridors were subjected to benchmarking, taking environmental aspects, infrastructure parameters, exhaust emissions and also external and internal costs into consideration. Finally, the utilisation of "green" technologies on the selected transport corridors was also analysed.